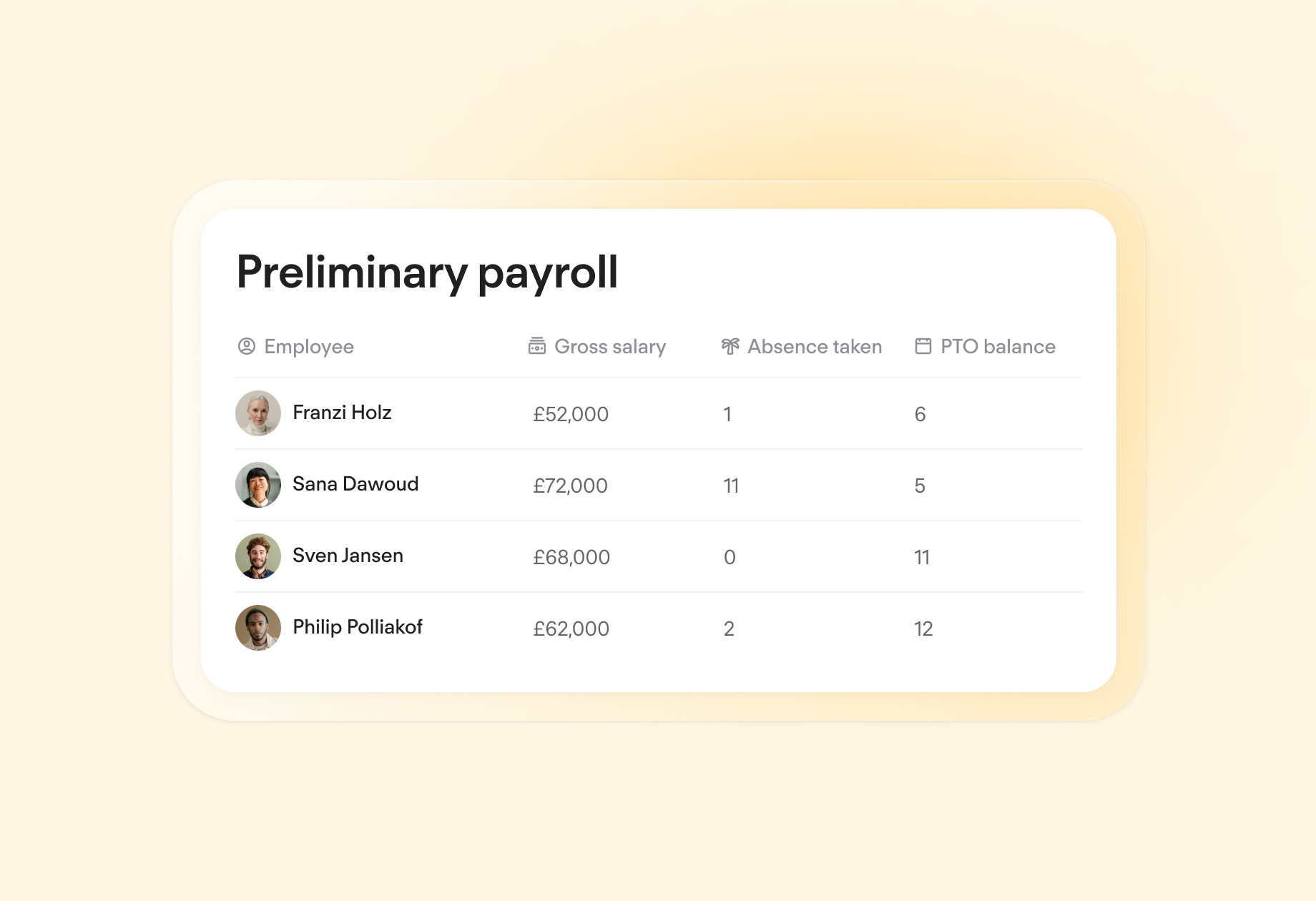
Start simplifying your payroll management
Learn how to streamline your payroll process to save time and ensure accuracy.
Read our guideUnderstanding Basic Salary and Base Pay in the UK
Have you ever been confused by the terms on a pay slip? With terms like basic pay, gross pay and net pay appearing without explanation, getting lost can be easy.
So, what is a basic salary? What is base pay? We explain these common terms and the factors that affect your basic salary. We also guide you through how your basic salary or base pay impact the amount of money you take home each pay period.
Key facts
Basic salary or base pay encompasses all fixed or guaranteed income associated with an employee's role.
Basic salary is sometimes stated in job advertisements and formalised in the employment contract once an individual accepts a job offer.
An employee’s base pay is different from their gross pay and net pay, each of which represent a calculation step in the payroll process.
What is the difference between basic salary and base pay?
Basic salary and base pay both refer to the amount you earn before any extra additions or deductions are made.
All fixed or guaranteed income is included in basic salary and base pay. For example, a guaranteed annual bonus payment would be part of basic salary. By contrast, a discretionary bonus is not part of basic salary because it is not guaranteed income.
What is basic salary?
Basic salary is the entire amount an employee is guaranteed to earn in exchange for their work, without regard to variable pay additions or deductions. In the UK, minimum wage and living wage regulations set the minimum standards for basic salary.
When salary is included on a job advertisement, it typically reflects the basic salary for the role. Once an individual is offered a job, the offer letter will include the basic salary. If the individual accepts the job and is hired, then their basic salary is formalised in the employment contract.
Additions and deductions to basic salary can make a large difference to how much an employee actually receives in their paycheque.
Possible additions to the basic salary
Additions may be communicated in the employment contract, or in company policies. Additions can include:
Discretionary bonus programmes
Allowances, such as travel expenses
Commission payments
Stock options or company shares
Other incentive pay, such as paid holidays or product vouchers
Overtime pay
Possible deductions from the basic salary
Deductions from basic salary often stem from legally required deductions, but can also come from voluntary programmes. Possible deductions include:
Tax and national insurance
Student loan repayments
Court ordered deductions, such as child maintenance
Union membership or deductions due to industrial action
Pension contributions
Charity donations
Childcare vouchers
Other salary sacrifice schemes, such as cycle-to-work schemes for bicycle purchase
Simplify your payroll tasks

Prepare your payroll more efficiently for accounts. Enable employees to change personal data themselves that HR approves. Working hours and bonus details are automatically transferred to your payroll system.
Streamline How You Pay EmployeesDifference between basic salary, gross salary and net salary
Gross salary consists of basic salary plus any additions. For example, if an employee earns a set annual salary, then that is their basic salary. If the same employee is paid a discretionary bonus, then their gross salary will equal the basic salary plus the amount of the bonus.
Basic salary and gross salary would be the same amount if an employee received no additions to their basic salary during the pay period.
Net pay, or net salary, is the amount actually paid to an employee after all additions and deductions have been made. Net pay is sometimes referred to as take home pay because it is the amount you take home after taxes and other adjustments.
Example of basic salary, gross salary and net salary
Alexandra earns a set annual salary of £37,000. She is also awarded a discretionary bonus of £1,000 and is repaying student loans.
Alexandra’s basic salary = £37,000
Alexandra’s gross salary = £38,000 (basic salary + £1,000 discretionary bonus)
Alexandra’s net salary = £28,428.40 (gross salary - £5,086 tax - £3051.60 national insurance - £1,434 student loan repayment)
Influences on your base pay
The amount offered as base pay can vary based on a number of factors. These factors include the job’s location, industry, role type, experience level, and seasonality.
Location
Where a job is based can significantly impact base pay. In the UK, different regions have varying costs of living, demand for certain skills, and local economic conditions. Generally, urban areas and larger cities tend to offer higher salaries due to the higher cost of living and increased competition for talent. For example, the average basic salary in the UK is £33,000, but that increases to almost £42,000 when looking only at London.
Role Type
Different roles within a company can have varying base pay levels. Roles that require greater responsibility, decision-making, and leadership tend to have higher base salaries. For example, managerial positions or roles that require niche technical expertise often come with higher compensation packages compared to entry-level or administrative roles.
Experience Level
An individual's experience level is a crucial factor in determining base pay. Generally, individuals with more years of relevant experience command higher salaries due to their proven track record and ability to contribute effectively. Many companies have structured pay scales that increase with each level of experience, reflecting the growing value an experienced employee brings to the organisation.
Seasonality
Some industries or roles may experience fluctuations in demand based on the time of year. For instance, retail positions may see increased demand during holiday seasons, while certain agricultural or tourism-related roles may be seasonal in nature. These fluctuations can affect base pay as employers may offer higher wages during peak seasons to attract temporary or part-time workers.
The bottom line on basic salary and base pay
Basic salary, or base pay, is the starting point for determining how much an employee receives in their paycheque. Additions and deductions are calculated during the payroll process that result in the employee’s net take home pay.
Make it easy for your employees to understand their pay and eliminate errors with Personio’s effortless payroll integration. Employees are empowered to view and download their pay slips and can even self-edit personal data, saving valuable admin time. Book a free demo today to see how Personio can simplify your HR and payroll tasks!
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Does the basic salary include pension?
Basic salary does not include employee pension contributions. The pension contribution will be deducted from basic salary as part of the payroll calculations used to arrive at the employee’s net take home pay.
What is base pay on a payslip?
On a payslip, base pay reflects the employee’s pay before any additions or deductions are factored in. This is the fixed amount of money that an employee earns for performing their regular job duties and excludes additional bonuses or other forms of compensation. It also excludes deductions like tax payments or salary sacrifice schemes.
What is the basic monthly salary?
Basic monthly salary is the fixed amount of money an employee earns each month before considering pay additions or deductions. For example, an employee earning an annual salary of £36,000 would see a monthly base salary on their payslip equal to £3,000 (£36,000 annual salary divided by 12 months).