Definition and Examples of Job Shadowing at Work

Through job shadowing, newer workers have access to an invaluable wealth of information on specific processes within the company that can drastically change their career paths. Below is a guide on this procedure to help you better understand it and utilise it within your company.
Key Facts
Job shadowing involves a guest, including a fellow employee, observing senior employees throughout their work day.
A well-run shadowing process strengthens bonds within the company by providing opportunities to learn and network.
Shadowing is at its most helpful when training a new hire in the ins and outs of their department.
Contents
What Is Job Shadowing?
Job shadowing is a form of on-the-job training used to aid the onboarding process by letting employees observe experienced workers performing a similar role.
Why Job Shadowing?
Job shadowing allows both parties to develop valuable skills and resources to help them further their career goals. Employees gain a first-row look into your company and its workings, while experienced employees learn important skills in mentorship and leadership.
Additionally, implementing job shadowing within your company helps create a more well-rounded workforce that can handle a wider range of challenges as they arise.
Below are a few advantages specific to the guest, the shadower, and the host, the employee being shadowed.
Benefits for the Host
Networking. Every coworker the host guides can expand their support network and lead to new professional opportunities to further their career.
Learning from different perspectives. Employees unfamiliar with the normal operation of the host's department could potentially provide valuable insights from their outside perspective, creating a robust collaborative learning experience.
Develops coaching skills. Guiding coworkers can help hosts identify the most important information to convey and the best way to deliver it to others without overwhelming them.
Opportunity for reflection. Job shadowing allows the host to refresh their knowledge of their department by answering the guest's inexperienced questions.
Benefits for the Guest
Learn the processes of another department. Guests can take what they learn from other departments or employees and apply it to their role.
Understand the contribution of other roles. If the guests are from another department, job shadowing can help them understand how other areas of the company contribute to its overall operation.
Receive expert advice. The guest can glean valuable insights from a more experienced employee that they couldn’t get from any job training video or online course.
Identify challenges and priorities. By pairing them with a more senior employee, new hires receive a comprehensive overview of company and departmental procedures. This allows them to identify key priorities and common challenges. That advanced knowledge lets them plan their work strategy before officially starting the job.
When Is Job Shadowing Most Beneficial?
One of the reasons that job shadowing is such an effective tool in the workplace is its versatility. Learning from a more experienced worker is not limited to a specific time or place. A few scenarios where shadowing is the most useful are listed below.
Onboarding
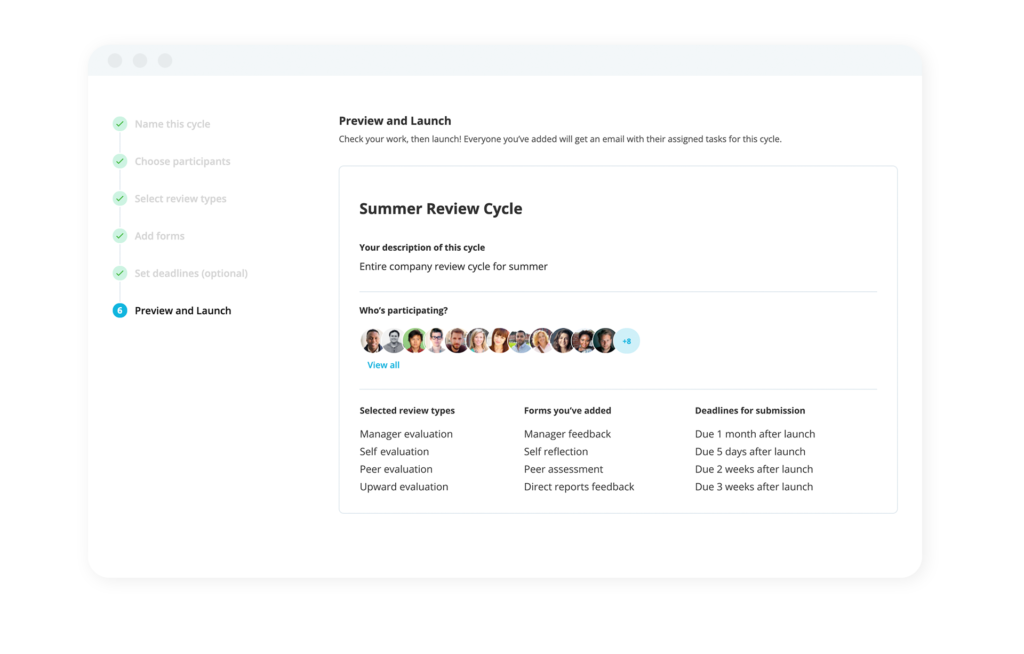
Companies often guide new hires to shadow senior employees to help them start their new positions as productively as possible. The host teaches them the foundational knowledge they’ll need to perform the basics of the job while warning them of common pitfalls or obstacles they’re likely to encounter. The guided introduction helps new workers better understand company operations while building a positive connection with the company through their host. Through job shadowing at onboarding, they also build important relationships early on with other employees.
Onboarding Software: For Seamless New Starts
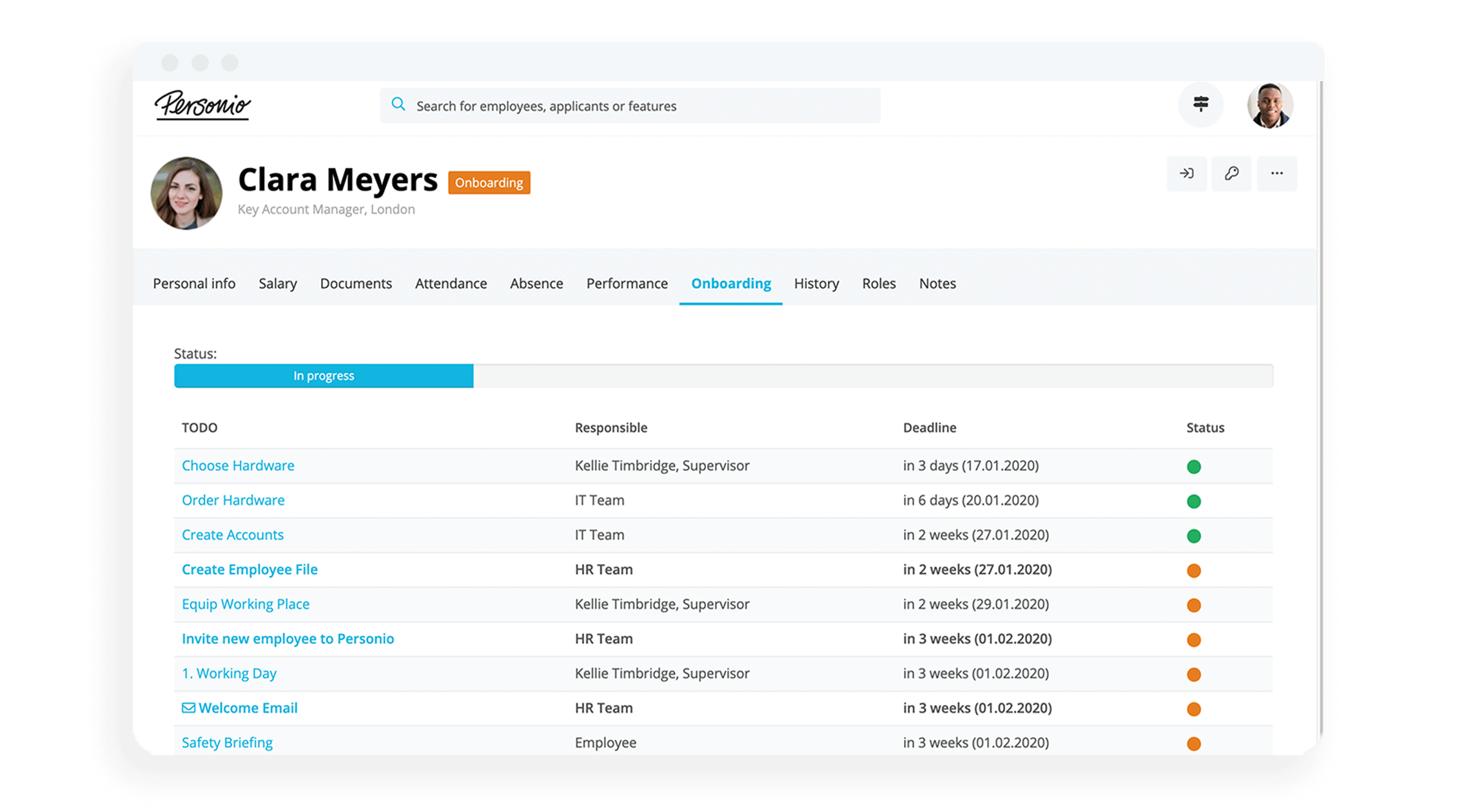
Give every new employee a flying start with Personio’s automated onboarding software, trusted by 15,000 happy customers across the UK and Europe.
Show me moreProfessional Development
Employees who want to advance within the company can use job shadowing to better understand the competencies needed in higher positions. It’s a common practice among HR professionals to assign interested workers to members of leadership as part of their professional development plan.
Cross-Training
Job shadowing can also be used to teach members of your workforce the processes and strategies of other departments. This can help foster a sense of unity among your staff by demonstrating the importance of different areas of the company. In addition, instruction from an experienced employee familiarises the shadower with the other department's processes, potentially enabling them to handle those responsibilities in an emergency.
Tips and Best Practices for Job Shadowing
You can use several methods to ensure that job shadowing is as effective as possible without disrupting your company’s standard workflow.
Setting up a shadowing process is relatively simple, but it can produce negligible or even negative results without careful consideration.
Vet Your Hosts
Not every senior employee is well-suited to a coaching role. It’s not enough to be knowledgeable about the department — the right host should be a good communicator, friendly and approachable.
Additionally, some employees may not be as interested in mentoring new hires as others and it’s important to respect that. The instruction trainees receive likely won’t be as comprehensive if you force a host into the role.
Instead, rely on volunteers or offer incentives to attract as many people as you need. With a pool of interested candidates, you can then pick out the people that best meet your expectations for the job shadowing initiative.
Develop a Concrete Plan
Help your hosts develop a schedule that makes the best use of their time. Make sure they can still accomplish most of their responsibilities while leaving time for them to answer their shadow’s questions.
Additionally, this is a good time to iron out the trainee's role in the host’s workday.
Do they get hands-on experience, or will they only observe? Do they need to prepare anything? Is there anything work-related they can’t interact with on their first day? Having answers to these questions helps ensure a smooth training experience.
Emphasise Confidentiality
If a new hire is exposed to sensitive information while shadowing a senior employee, ensure they understand the importance of confidentiality first. Many companies work to avoid those scenarios, but sometimes a host’s schedule can’t accommodate discretion. You can make them sign an NDA or disallow them from participating in their host’s more critical responsibilities.
Encourage Guest Participation
The primary motivation behind job shadowing is to provide a positive learning experience for the guest, so their mentor must answer all of their questions. From there, you can have them fill out a survey or write a summary of what they learned, so the host can see if there are any gaps in their knowledge. The final review can help clarify any information the guest received, while their fresh perspective could provide helpful insights into current company operations.
Review The Process and Revise
After every shadowing, hold a meeting with the guest and gather feedback about their experience with the programme. This can help you find weak points in the process and develop new and more effective ideas for the future.
Ensure your EVP matches your culture

The culture of your company is going to have a monumental impact on your EVP and how you attract the best talent. Click here for our guide to building your corporate culture.
Get the guideHow Does the Host Prepare for Job Shadowing?
There are several preparations that a host should make before being shadowed to ensure that the process goes as smoothly as possible. Some of those things include:
Inform the trainee when the shadowing will start and where it will take place.
Brief coworkers about the shadowing and enlist their help where needed.
Carve out time in the schedule for the guest to ask questions.
Ensure the trainee has adequate information about the department before they begin their observation.
Provide a notice, including the reasoning, if the shadowing has to be postponed or cancelled.
Offer constructive feedback on how the trainee conducts themselves in the workplace.
How Does the Guest Prepare for Job Shadowing?
There are also several things that the guest can prepare to get the most out of their job shadowing. Some of those things are:
Outline your expectations for the job shadowing to help your mentor guide the experience to where you most need it to go.
Behave professionally and offer to withdraw from situations that seem to involve discretion.
Avoid sharing any confidential information learned while shadowing a senior employee.
Offer constructive criticism when the job shadowing is complete.
If you can’t attend the shaping, inform the host and relevant company members beforehand so they can change their schedules.
Frequently Asked Questions About Job Shadowing
What Is an Example of Job Shadowing?
Job shadowing can be someone observing client interactions or letting the shadow perform less essential tasks in the workplace under direct supervision.
What Are the 3 Types of Job Shadowing?
The three types of shadowing are:
Observation
Regular Briefings
Hands-on
Build a More Flexible Workforce Today
There are few better ways to learn than receiving hands-on experience with company processes or observing how a pro does it. Job shadowing helps build an effective process for transferring knowledge from one senior employee down. Whether the guest is a new hire or someone interested in learning how the rest of the company operates, shadowing makes an excellent addition to any professional growth plan.
Disclaimer
We would like to inform you that the contents of our website (including any legal contributions) are for non-binding informational purposes only and does not in any way constitute legal advice. The content of this information cannot and is not intended to replace individual and binding legal advice from e.g. a lawyer that addresses your specific situation. In this respect, all information provided is without guarantee of correctness, completeness and up-to-dateness.